Nation ramps up efforts in shale gas discovery to enhance energy security


China is intensifying its shale gas development efforts as a cornerstone of its strategy to enhance energy security and facilitate a transition toward cleaner energy sources, with recent breakthroughs underscoring the nation's advancements in unlocking unconventional gas reserves.
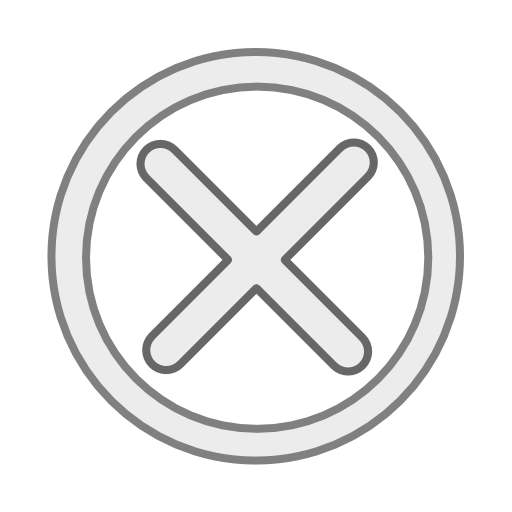
China's largest shale gas production base in the southern Sichuan Basin, Southwest China's Sichuan province, has achieved a cumulative output exceeding 100 billion cubic meters, PetroChina Southwest Oil and Gasfield Co, a subsidiary of China National Petroleum Corp, said on Wednesday.
This milestone marks the first time a Chinese shale gas field has surpassed this production level, solidifying its position as a critical contributor to the nation's energy mix, it said.
Adding to the momentum, China Petroleum and Chemical Corp, also known as Sinopec, announced on the same day that test production at two evaluation wells in its Ziyang shale gas field, also located in Sichuan province, had exceeded one million cubic meters.
The Ziye 2-501HF well, in particular, demonstrated exceptional performance, producing 1.407 million cubic meters per day during testing, setting a new national benchmark for shale gas well productivity, said the company, the world's largest refiner.
The results demonstrate the potential for efficient development of ultra-deep shale gas in the Sichuan Basin, which is strategically important for China's energy security, it said.
China, rich in coal resources but lacking in gas, has long been a major importer of oil and gas. The exploration and development of shale gas is of strategic importance for China's energy landscape, Sinopec said.
According to BloombergNEF, shale gas has firmly established itself as a cornerstone of China's energy security, supporting the nation's shift toward cleaner, more resilient energy systems.
Shale gas is playing a key role in boosting unconventional gas production, whose growth is on track to outpace conventional gas, it said.
The success in the Sichuan Basin is particularly noteworthy given the complex geological challenges inherent in the region, including deep burial depths, thin shale layers and intricate fault systems, which historically have hindered efficient gas extraction.
Chinese oil and gas companies, however, have overcome these obstacles through the development and implementation of cutting-edge technologies.
Key technological advances, including sophisticated 3D geological modeling, which provides a detailed understanding of subsurface formations, optimized drilling techniques and precision fracturing methods, have enabled efficient extraction from previously inaccessible and challenging reserves.
This substantial resource base and extensive infrastructure solidify the region's role as a cornerstone of China's energy security and a major driver of future gas supply growth.
The exploration and development of shale gas is therefore of strategic importance for China's energy landscape, which is relatively rich in coal resources but has limited conventional oil and gas reserves, enabling the country to diversify its energy sources, reduce its reliance on imports and enhance its overall energy security, said industry experts.
Furthermore, shale gas, which is primarily composed of methane, is considered a cleaner-burning fuel than coal, making it a valuable component of China's energy transition strategy.
"China's drive for energy independence hinges on boosting domestic oil and gas production through technological advances. This is strengthening the world's second-largest economy's energy security," said Lu Ruquan, head of the CNPC Economics and Technology Research Institute.
Chinese oil and gas companies are aggressively investing in both conventional and unconventional energy to expand reserves and improve efficiency, he said.
Lu highlighted that the three major players — CNPC, China National Offshore Oil Corp and Sinopec — have all increased exploration and development investment in recent years, leading to significant discoveries.
These efforts demonstrably reduced China's reliance on crude oil imports in 2024, with the sector showing considerable strength by leveraging advanced technologies to increase domestic production and reduce dependence on foreign sources, he added.
Figures released by the institute reveal that China's total oil and gas output surpassed 400 million metric tons of oil equivalent last year, while total power generation exceeded 10 trillion kilowatt-hours, marking a 5.7 percent increase over the previous year.
zhengxin@chinadaily.com.cn